Java JList
The object of JList class represents a list of text items. The list of text items can be set up so that the user can choose either one item or multiple items. It inherits JComponent class.
JList class declaration
Let's see the declaration for javax.swing.JList class.
- public class JList extends JComponent implements Scrollable, Accessible
Commonly used Constructors:
| Constructor | Description |
|---|
| JList() | Creates a JList with an empty, read-only, model. |
| JList(ary[] listData) | Creates a JList that displays the elements in the specified array. |
| JList(ListModel<ary> dataModel) | Creates a JList that displays elements from the specified, non-null, model. |
Commonly used Methods:
| Methods | Description |
|---|
| Void addListSelectionListener(ListSelectionListener listener) | It is used to add a listener to the list, to be notified each time a change to the selection occurs. |
| int getSelectedIndex() | It is used to return the smallest selected cell index. |
| ListModel getModel() | It is used to return the data model that holds a list of items displayed by the JList component. |
| void setListData(Object[] listData) | It is used to create a read-only ListModel from an array of objects. |
Java JList Example
- import javax.swing.*;
- public class ListExample
- {
- ListExample(){
- JFrame f= new JFrame();
- DefaultListModel<String> l1 = new DefaultListModel<>();
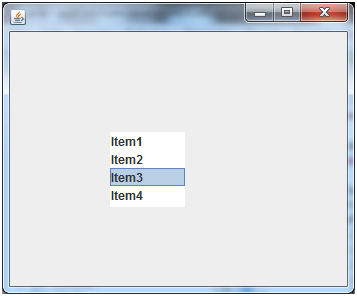
- l1.addElement("Item1");
- l1.addElement("Item2");
- l1.addElement("Item3");
- l1.addElement("Item4");
- JList<String> list = new JList<>(l1);
- list.setBounds(100,100, 75,75);
- f.add(list);
- f.setSize(400,400);
- f.setLayout(null);
- f.setVisible(true);
- }
- public static void main(String args[])
- {
- new ListExample();
- }}
Output:
Java JList Example with ActionListener
- import javax.swing.*;
- import java.awt.event.*;
- public class ListExample
- {
- ListExample(){
- JFrame f= new JFrame();
- final JLabel label = new JLabel();
- label.setSize(500,100);
- JButton b=new JButton("Show");
- b.setBounds(200,150,80,30);
- final DefaultListModel<String> l1 = new DefaultListModel<>();
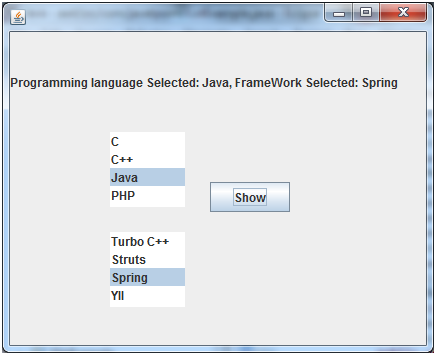
- l1.addElement("C");
- l1.addElement("C++");
- l1.addElement("Java");
- l1.addElement("PHP");
- final JList<String> list1 = new JList<>(l1);
- list1.setBounds(100,100, 75,75);
- DefaultListModel<String> l2 = new DefaultListModel<>();
- l2.addElement("Turbo C++");
- l2.addElement("Struts");
- l2.addElement("Spring");
- l2.addElement("YII");
- final JList<String> list2 = new JList<>(l2);
- list2.setBounds(100,200, 75,75);
- f.add(list1); f.add(list2); f.add(b); f.add(label);
- f.setSize(450,450);
- f.setLayout(null);
- f.setVisible(true);
- b.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
- public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
- String data = "";
- if (list1.getSelectedIndex() != -1) {
- data = "Programming language Selected: " + list1.getSelectedValue();
- label.setText(data);
- }
- if(list2.getSelectedIndex() != -1){
- data += ", FrameWork Selected: ";
- for(Object frame :list2.getSelectedValues()){
- data += frame + " ";
- }
- }
- label.setText(data);
- }
- });
- }
- public static void main(String args[])
- {
- new ListExample();
- }}
Output:


0 comments:
Post a Comment