Java AWT Button
A button is basically a control component with a label that generates an event when pushed. The Button class is used to create a labeled button that has platform independent implementation. The application result in some action when the button is pushed.
When we press a button and release it, AWT sends an instance of ActionEvent to that button by calling processEvent on the button. The processEvent method of the button receives the all the events, then it passes an action event by calling its own method processActionEvent. This method passes the action event on to action listeners that are interested in the action events generated by the button.
To perform an action on a button being pressed and released, the ActionListener interface needs to be implemented. The registered new listener can receive events from the button by calling addActionListener method of the button. The Java application can use the button's action command as a messaging protocol.
AWT Button Class Declaration
Button Class Constructors
Following table shows the types of Button class constructors
Button Class Methods
| Sr. no. | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | void setText (String text) | It sets the string message on the button |
| 2. | String getText() | It fetches the String message on the button. |
| 3. | void setLabel (String label) | It sets the label of button with the specified string. |
| 4. | String getLabel() | It fetches the label of the button. |
| 5. | void addNotify() | It creates the peer of the button. |
| 6. | AccessibleContext getAccessibleContext() | It fetched the accessible context associated with the button. |
| 7. | void addActionListener(ActionListener l) | It adds the specified action listener to get the action events from the button. |
| 8. | String getActionCommand() | It returns the command name of the action event fired by the button. |
| 9. | ActionListener[ ] getActionListeners() | It returns an array of all the action listeners registered on the button. |
| 10. | It returns an array of all the objects currently registered as FooListeners upon this Button. | |
| 11. | protected String paramString() | It returns the string which represents the state of button. |
| 12. | protected void processActionEvent (ActionEvent e) | It process the action events on the button by dispatching them to a registered ActionListener object. |
| 13. | protected void processEvent (AWTEvent e) | It process the events on the button |
| 14. | void removeActionListener (ActionListener l) | It removes the specified action listener so that it no longer receives action events from the button. |
| 15. | void setActionCommand(String command) | It sets the command name for the action event given by the button. |
Note: The Button class inherits methods from java.awt.Component and java.lang.Object classes.
Java AWT Button Example
Example 1:
ButtonExample.java
import java.awt.*;
public class ButtonExample {
public static void main (String[] args) {
// create instance of frame with the label
Frame f = new Frame("Button Example");
// create instance of button with label
Button b = new Button("Click Here");
// set the position for the button in frame
b.setBounds(50,100,80,30);
// add button to the frame
f.add(b);
// set size, layout and visibility of frame
f.setSize(400,400);
f.setLayout(null);
f.setVisible(true);
}
To compile the program using command prompt type the following commands
If there's no error, we can execute the code using:
Output:
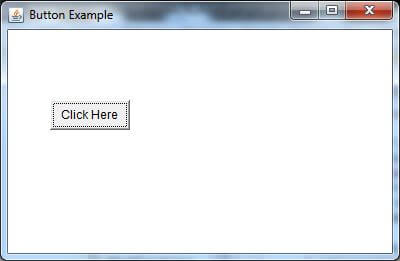
Example 2:
Output:
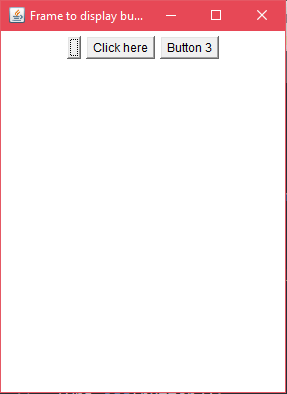
Java AWT Button Example with ActionListener
Example:
In the following example, we are handling the button click events by implementing ActionListener Interface.
ButtonExample3.java
// importing necessary libraries
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class ButtonExample3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create instance of frame with the label
Frame f = new Frame("Button Example");
final TextField tf=new TextField();
tf.setBounds(50,50, 150,20);
// create instance of button with label
Button b=new Button("Click Here");
// set the position for the button in frame
b.setBounds(50,100,60,30);
b.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed (ActionEvent e) {
tf.setText("Welcome to Javatpoint.");
}
});
// adding button the frame
f.add(b);
// adding textfield the frame
f.add(tf);
// setting size, layout and visibility
f.setSize(400,400);
f.setLayout(null);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
Output:
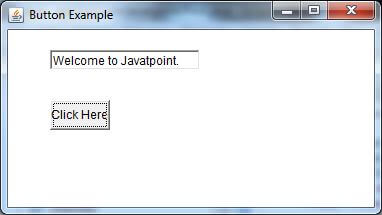
0 comments:
Post a Comment