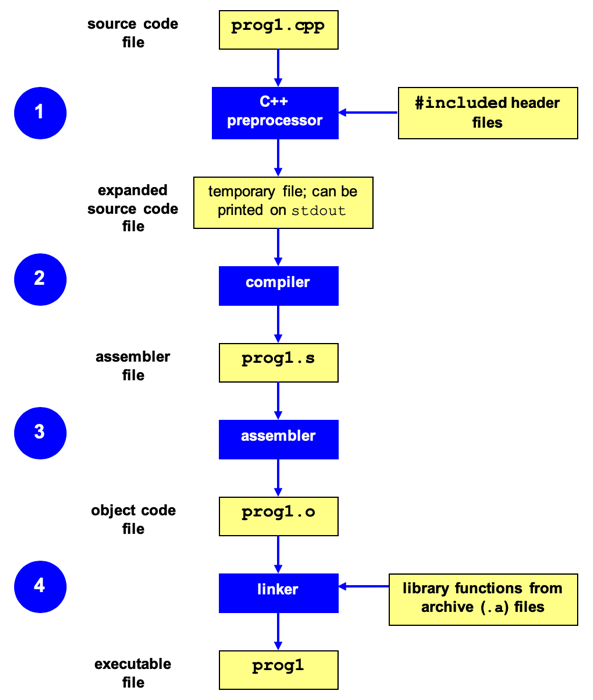
Stages of Compilation in C++
The process of compilation in C++ can be divided into four primary stages: Preprocessing, Compilation, Assembly, and Linking. Each stage performs a specific task, ultimately converting the source code into an executable program.
Preprocessing
The first stage is the preprocessing of the source code. Preprocessors modify the source code before the actual compilation process. They handle directives that start with a # (hash) symbol, like #include, #define, and #if. In this stage, included header files are expanded, macros are replaced, and conditional compilation statements are processed.
Code Example:
#include <iostream>
#define PI 3.14
int main() {
std::cout << "The value of PI is: " << PI << std::endl;
return 0;
}Compilation
The second stage is the actual compilation of the preprocessed source code. The compiler translates the modified source code into an intermediate representation, usually specific to the target processor architecture. This step also involves performing syntax checking, semantic analysis, and producing error messages for any issues encountered in the source code.
Code Example:
int main() {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int sum = a + b;
return 0;
}Assembly
The third stage is converting the compiler’s intermediate representation into assembly language. This stage generates assembly code using mnemonics and syntax that is specific to the target processor architecture. Assemblers then convert this assembly code into object code (machine code).
Code Example (x86 Assembly):
mov eax, 10
mov ebx, 20
add eax, ebxLinking
The final stage is the linking of the object code with the necessary libraries and other object files. In this stage, the linker merges multiple object files and libraries, resolves external references from other modules or libraries, allocates memory addresses for functions and variables, and generates an executable file that can be run on the target platform.
Code Example (linking objects and libraries):
$ g++ main.o -o main -lmIn summary, the compilation process in C++ involves four primary stages: preprocessing, compilation, assembly, and linking. Each stage plays a crucial role in transforming the source code into an executable program.
0 comments:
Post a Comment